Also known as methyl alcohol or wood naphtha – is the simplest alcohol with the formula CH3OH. The reference to “wood alcohol” derives from its original method of synthesis via distillation of wood. This ancient method is no longer used, and the current process relies on a more effective catalytic reaction between carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H).
Methanol forms a volatile and flammable colourless solution with a characteristic alcohol smell.
Unlike its “cousin” ethanol, ingestion of methanol can be extremely dangerous, as its metabolism forms formic acid and formate salts, which are poisonous to the nervous system.
 Methanol’s most common uses
Methanol is an extremely popular compound, with multiple industrial applications, including:
Methanol’s most common uses
Methanol is an extremely popular compound, with multiple industrial applications, including:
Reagent in several processes: probably, the most common use for methanol is as an ingredient in different industrial reactions, in which it’s converted to other chemicals (see table). For example, it can be converted to formaldehyde during the process of manufacture of paints, explosives or plastics, to name just a few. Other derivatives include dimethyl ether, an aerosol spray propellant to replace CFCs;acetic acid and methyl mercaptan.
Formaldehyde |
Adhesives used in particle board, plywood, and other wood products. Spandex fibres, thermoplastics, urethane foams used in seats, bumpers and body panels of cars |
Acetic Acid |
PET (clear) plastic packaging, carpet and clothing fibre. |
Methylamines |
Liquid detergents, shampoos, solvents, water-treatment chemicals. |
Methyl Methacrylate (acrylics) |
Water-based paints and coatings, appliance & automotive plastics. |
Methyl Mercaptan |
Jet fuel additive. |
Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) |
Beverage bottles, polyester fabrics |
MTBE (Methyl-Tertiary Butyl Ether) |
Gasoline octane booster, primarily in Europe and Asia. |
FUEL Pure methanol can be used directly in internal combustion engines, including in vehicles and aircrafts, with similar efficiency to diesel engines. One of the problems with this application is the high corrosion caused by methanol, particularly against aluminium.
Pure methanol can be used directly in internal combustion engines, including in vehicles and aircrafts, with similar efficiency to diesel engines. One of the problems with this application is the high corrosion caused by methanol, particularly against aluminium.
Manufacturers are trying to develop methanol-resistant materials as well as additives which may be able to counteract this type to corrosion. For many, this would the ideal alternative to fossil fuel to be used in the future, as internal combustion engines can be adapted easily, it’s safe and easily biodegradable in case of accident and can be produced from renewable sources. Maybe it’s the fuel of the future!
Biodiesel Methanol – and less commonly ethanol – can be used to produce biodiesel, in a reaction of transesterification of lipids (see figure). This product may be used in its pure form or blended with petroleum diesel.
Denaturing agent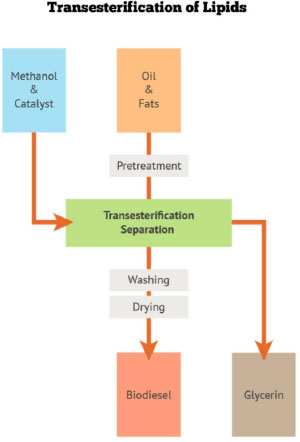 Traditionally, methanol is used as a denaturing agent added to synthetic ethanol to prevent its consumption.
Traditionally, methanol is used as a denaturing agent added to synthetic ethanol to prevent its consumption.
Waste water treatment:
Small amounts of methanol can be used in wastewater, as a source of carbon to bacteria converting harmful nitrates to safer nitrogen, thus reducing the dangers of nitrification.
Solvent:
Both in the lab and in many industrial settings, methanol is the solvent of choice for many applications.
Denaturing agent (2):
Remaining in the lab, methanol is also used in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis as a denaturing agent. In addition, methanol can be used in HPLC and spectroscopy.
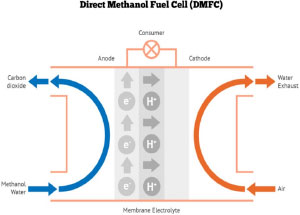
Direct-methanol fuel cells:
These are proton-exchange cells which rely on methanol as fuel. They are easy to produce and can easily be scaled down, potentially opening the door to its application to power small appliances, such as mobile phone or laptop. Basically these cells are characterised by the oxidation of methanol to form carbon dioxide.
CH3OH + 3/2 O2 -> 2 H2O + CO2
Water methanol injection: In some high performance internal combustion engines, a mixture of water and methanol is sprayed into the fuel or cylinder to cool the system down. In this case, the methanol is added to keep prevent the water from freezing. This system is known as anti-detonant injection, MW50 or simply methanol injection.
In some high performance internal combustion engines, a mixture of water and methanol is sprayed into the fuel or cylinder to cool the system down. In this case, the methanol is added to keep prevent the water from freezing. This system is known as anti-detonant injection, MW50 or simply methanol injection.